A business can expect a big impact on its profits if it doesn’t account for the depreciation of its assets. Depreciation is an accounting practice used to spread the cost of a tangible asset, such as a vehicle, piece of equipment, or property, over its useful life. It represents how much of the asset’s value has been used up in any given time period. In addition, there is another technique called the double-declining balance method that allows for an asset to be depreciated even faster, based on its straight-line depreciation amount multiplied by 200%. Accumulated depreciation is used to calculate an asset’s net book value, which is the value of an asset carried on the balance sheet.
What is your current financial priority?
The depreciation calculator uses three different methods to estimate how fast the value of an asset decreases over time. Depreciation is how an asset’s book value is « used up » as it helps to generate revenue. In the case of the semi-trailer, such uses could be delivering goods to how twitter and facebook think they handled the election customers or transporting goods between warehouses and the manufacturing facility or retail outlets. All of these uses contribute to the revenue those goods generate when they are sold, so it makes sense that the trailer’s value is charged a bit at a time against that revenue.
- This amount will be depreciated over its useful life using an appropriate depreciation method (e.g., straight-line, declining balance, etc.).
- By understanding and applying various methods such as straight-line, declining balance, and units of production, you can accurately allocate the cost of your assets over their useful lives.
- Learn how to calculate your depreciable cost, the depreciable cost formula, and how Enerpize can help you calculate your depreciable.
- That boosts income by $1,000 while making the balance sheet stronger by the same amount each year.
- The market value of the asset may increase or decrease during the useful life of the asset.
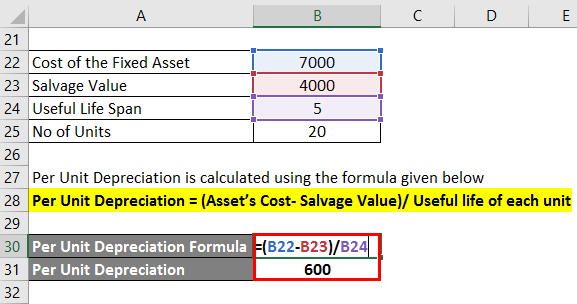
How the Straight-Line Method Is Calculated
It also keeps the asset portion of the balance sheet from declining as rapidly, because the book value remains higher. Both of these can make the company appear « better » with larger earnings and a stronger balance sheet. The expected useful life is another area where a change would impact depreciation, the bottom line, and the balance sheet. Suppose that the company is using the straight-line schedule originally described.
How Does Depreciation Impact the Financial Statements?
Leveraging this knowledge can give you a competitive edge in managing your business’s finances and driving sustainable growth. For larger businesses, incorporating depreciation calculations with ERP systems can provide a comprehensive understanding of financial operations. This multi-method approach can provide a more accurate overall picture of your business’s asset depreciation.
As the book value decreases over time, so does the depreciation expense, creating a “declining” pattern. By carefully considering these factors and gathering the necessary information, you’ll be well-prepared to calculate depreciation expense accurately. This preparation ensures that your financial statements reflect a true and fair view of your business’s asset values and overall financial position.

It’s an accelerated method for calculating depreciation because it allows larger depreciation write-offs in the early years of the asset’s useful life. Regardless of the depreciation method used, the total amount of depreciation expense over the useful life of an asset cannot exceed the asset’s depreciable cost (asset’s cost minus its estimated salvage value). The units of production method assigns an equal expense rate to each unit produced.
There are several different depreciation methods, including straight-line depreciation and accelerated depreciation. The Units of Production method offers a practical approach to calculating depreciation expense for assets whose depreciation is closely tied to their usage rather than time. This activity-based method provides a more accurate representation of an asset’s wear and tear based on its actual use. By understanding and applying the Sum-Of-The-Years’ Digits method, you’ll have a versatile tool for calculating depreciation expense that offers a balanced approach between straight-line and declining balance methods. By mastering the straight-line method, you’ll have a reliable tool for calculating depreciation expense that aligns with accounting standards and provides a clear picture of your assets’ declining value over time. This method’s simplicity and consistency make it an excellent starting point for business owners looking to implement a depreciation strategy.
The Section 179 deduction allows businesses to immediately deduct the full purchase price of eligible assets in the year they are put into service, up to an annual limit. Using MACRS can generate larger deductions compared to the straight-line method, reducing taxable income in early years. Businesses should evaluate their cash flow timeline to leverage these accelerated tax savings.

Commentaires récents